Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent

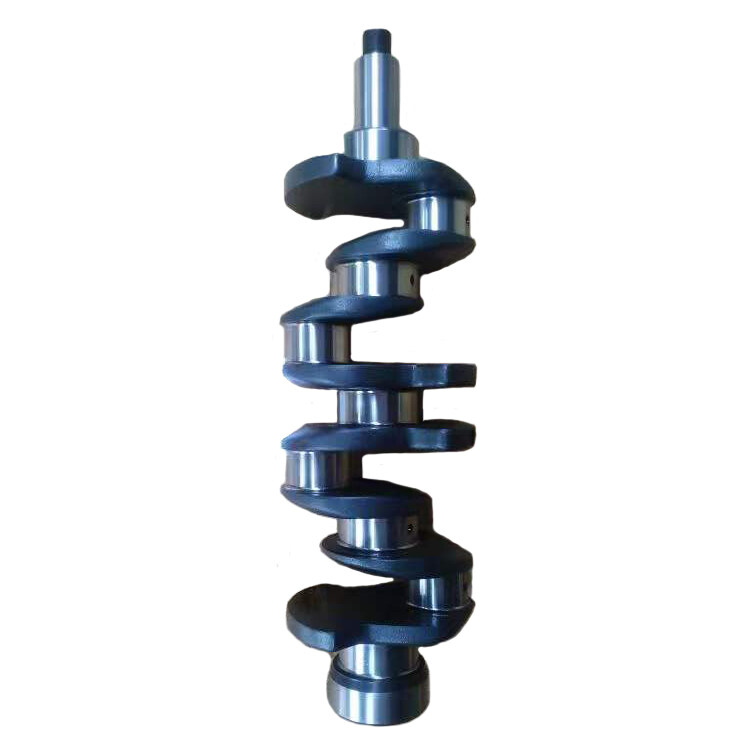
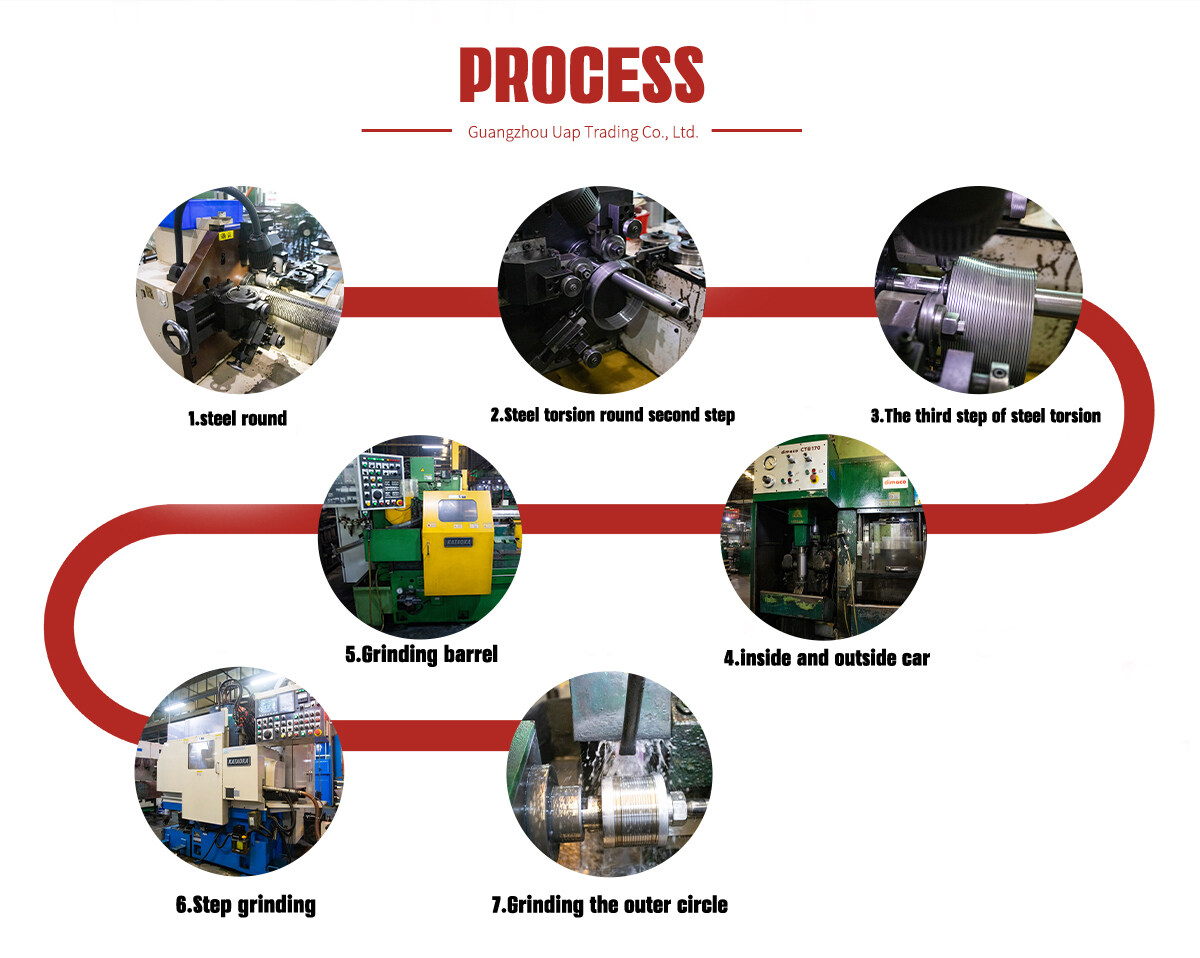
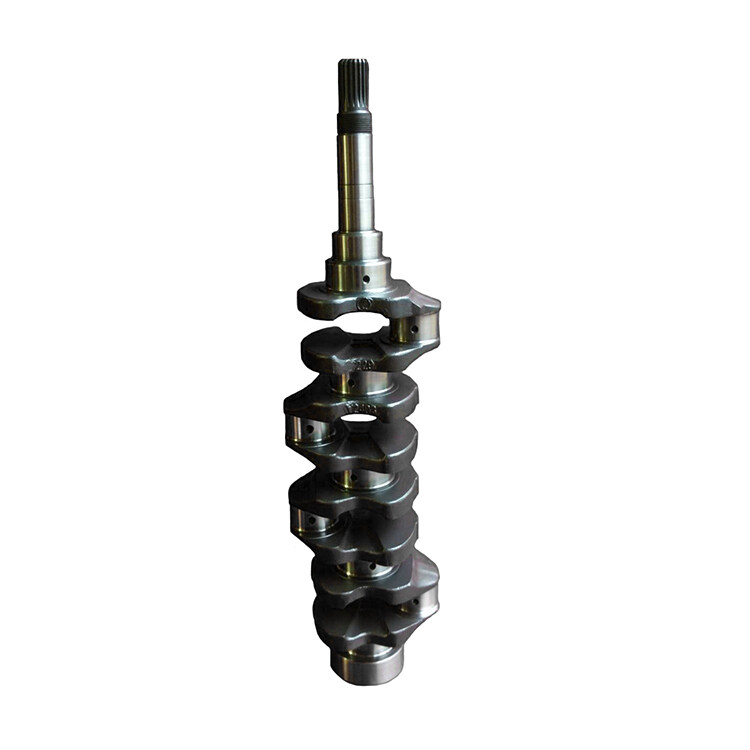
V2403 Diesel Engine Crankshaft 16641-23020
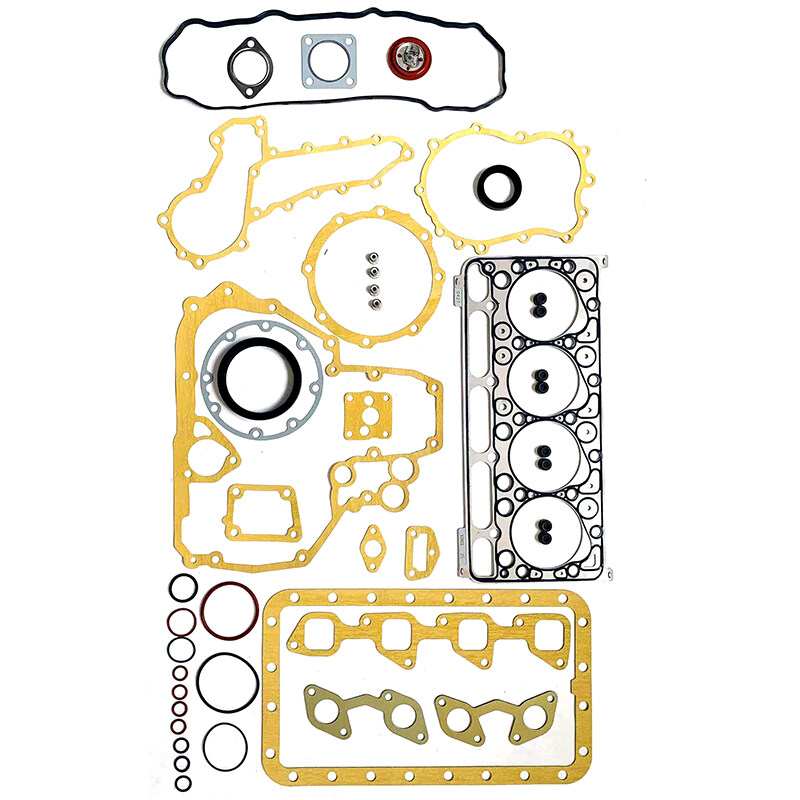
A liner kit for a 4BE1 diesel engine typically includes a set of cylinder liners, which are essential components used to provide a smooth, durable inner surface for the engine's cylinder bores.
The 4BE1 engine is commonly used in various industrial and commercial applications. Here's an overview of the components and functions of a liner kit:
Cylinder Liners: Cylinder liners, also known as cylinder sleeves, are the main components included in the kit. These liners are inserted into the engine's cylinder bores and serve several critical functions:
- Provide a smooth and wear-resistant surface for the engine's pistons to move within.
- Create a proper seal with the piston rings to maintain compression in the cylinder.
- Assist in heat dissipation, preventing overheating within the engine.
- Contribute to wear resistance and durability, particularly in high-stress diesel engines.
When it comes to the 4BE1 Diesel Engine Liner Kit, it's essential to ensure that the included cylinder liners are of high quality and designed to be compatible with the specific 4BE1 engine model. Proper installation, sizing, and fitting of the liners are necessary to ensure that they function correctly and provide a reliable seal for the engine's cylinders.
Product Parameter:
|
Product Name |
Engine Crankshaft |
|
Application |
Engineering Machinery Engine |
|
OEM Number |
16641-23020 |
|
Engine Number |
V2403 |
|
Car Model |
Kubota |
|
Condition |
100% Brand-new |
|
Warranty |
6 Months |
|
Packing |
Neutral / OEM |
|
Application Industries |
Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Repair Shops, Retail, Construction Works |
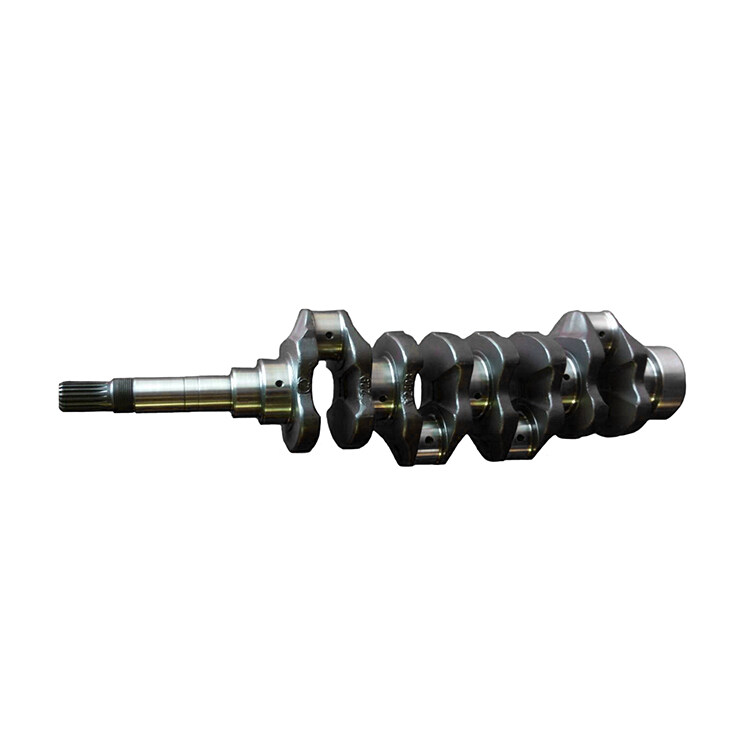
The crankshaft of the engine is designed with anti-corrosion and high-temperature resistant materials, ensuring that it is protected from corrosion and oxidation. With excellent hardness and strength, it can operate smoothly even under high-speed conditions, effectively preventing wear and tear. Additionally, its lightweight design ensures that it does not add unnecessary weight to the engine, allowing it to operate efficiently.
The Balance Design of Crankshaft Improves the Stability and Comfort of Engines:
The crankshaft is designed with a balanced design, which effectively reduces vibration and noise, and improves the stability and comfort of the engine. The balanced design ensures that the crankshaft rotates smoothly and evenly, reducing the amount of vibration and noise generated during operation. This not only improves the overall performance of the engine but also enhances the comfort of the operator. The reduced vibration and noise levels also help to extend the lifespan of the engine by reducing the wear and tear on its components.
Its Modular Design is Easy to Maintain:
The crankshaft is designed with a modular design, which makes it easy to disassemble and maintain. This design allows for quick replacement and repair of individual components, reducing maintenance costs and time. The modular design also simplifies the maintenance process, making it easier for technicians to identify and address any issues that may arise. This not only reduces the amount of time required for maintenance but also helps to minimize downtime and increase the overall efficiency of the engine. Additionally, the modular design of the crankshaft ensures that it can be easily adapted to different applications and environments, making it a versatile and reliable component for a wide range of diesel engines.
FAQ:
Q1:Are you factory or trade company?
Re: We are from factory, researching and developing the engine parts with more than 10 years.
Q2: Do you support OEM or ODM service?
Re: Yes, we support.
Q3: Do you support sample?
Re: We can send you with one sample if it is in stock, and you need to pay related fees.
What is a Crankshaft?
A crankshaft is a mechanical unit that transforms the reciprocating movement of the piston into rotary motion. A crankshaft connects to the piston through a connecting rod. The main objective of this connecting rod is to receive reciprocating motion by the piston and delivers it to the crankshaft.
As the crankshaft gets motion by the connecting rod, it transforms this motion into rotary motion and rotates the flywheel, which further moves the vehicle wheels.
Without a crank, a reciprocating engine is unable to deliver piston’s reciprocating to the drive shaft. In simple words, a reciprocating engine can’t move a vehicle without a crankshaft.
The crankshaft works on the crank mechanism. It is located inside the block of the engine. The crank includes in the moving components of the IC engine. It has many crankpins and cranks. The engine connecting rod attaches with the crank through these crankpins and cranks.
Working of Crankshaft
A crankshaft works on the crank mechanism. A crank has crankpins and cranks which are connected with the connecting rods. It has a vibration damper that reduces the thrust on the crank.

What are the reasons of the Crankshaft break?
The most common reasons for the crankshaft break are given below:
1.The crankshaft may break due to overloading through water hammer, abnormal combustion, etc.
2.Defective shaft material can also damage the crankshaft
3.An unexpected engine jam because of loose counterweight, and gearbox failure, etc.
4.The shaft’s mechanically damaging before fixing.
5.Unnecessary rotation and vibration due to clutch failure, defective flywheel, or damaged vibration damper.
6.Insufficient improvement work on the crankshaft bearings.
7.Material damage because of earlier bearing failure and annealed bearing journals, etc.
8.The bearing journal has become soft as a result of premature bearing failure or improper repair work (e.g., unnecessary regrinding).
9.The commissioning of the engine did not correspond to the manufacturer’s instructions.
10.Use of wrong bearing shell.
11.The old bearing head bolts or improper torque are utilized.
12.Too little lubricant during commissioning because the oil system is not pre-filled and pre-compressed.
13.Bearing caps of the connecting rod/main bearing were mixed or fixed crooked.
14.The crankcase bearing’s bore size inside the crankshaft was not inspected or repaired after damage.
15.The oil filter, engine oil, and oil cooler have not been changed on time.
16.If the bearing is damaged, the swarf that remains in the engine oil circuit can also cause the crankshaft to break.
How does a crankshaft break?
There is a mechanical concept called fatigue. It means that a material can fail due to repetitive loading. Each time crankshafts rotate, the loads reverse causes a slight flexing of the shaft. It’s much like how you can break a coat hanger or wire by merely bending it back a fourth, maybe a dozen times, and the wire breaks.
The flex of a crankshaft is much less, so millions of cycles are required to break it, but the failure mode is the same as the coat hanger. Now, if a bearing supporting the crankshaft fails due to a lack of lubrication, the deflection displacement per rotation dramatically increases so that failure can occur very quickly.

Another reason for the crankshaft failure is, that an unbalanced flywheel/torque converter or misaligned transmission will be high on the list of a break at the rear of a crank.
A stress riser (nick in the finely ground finish) in the radius next to the bearing journal may also cause of shaft break. The nick can turn into a crack that will propagate quickly.